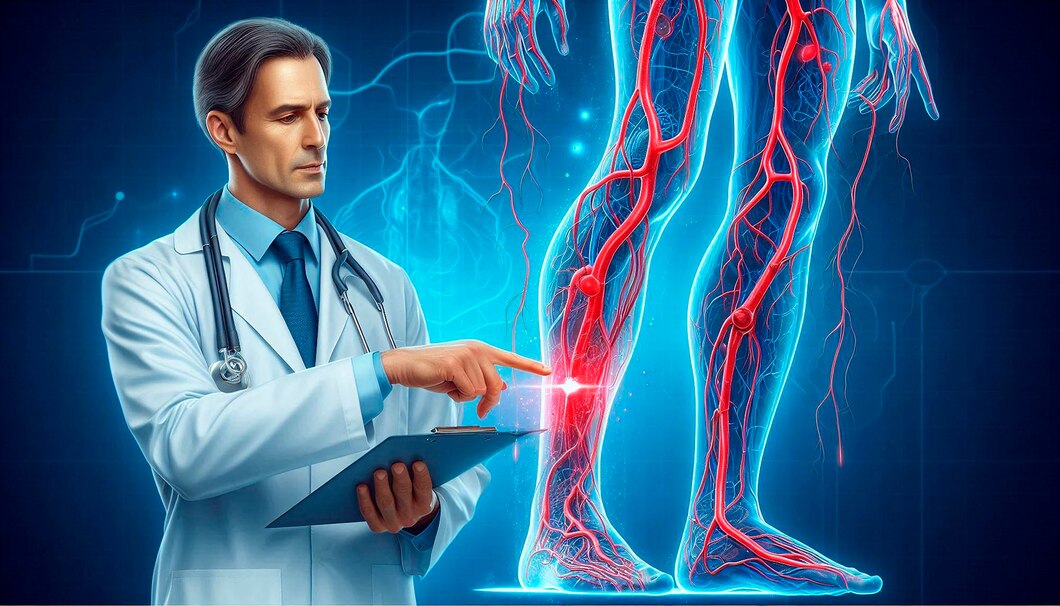
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This can lead to serious complications if the clot travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure vein health.
Symptoms of DVT
Swelling: Usually in one leg.
Pain or Tenderness: Often starts in the calf.
Warmth and Redness: Affected area may feel warm to the touch and appear red or discolored.
Leg Fatigue: Feeling of heaviness or tiredness in the affected leg.