Understanding Thyroid Goitre
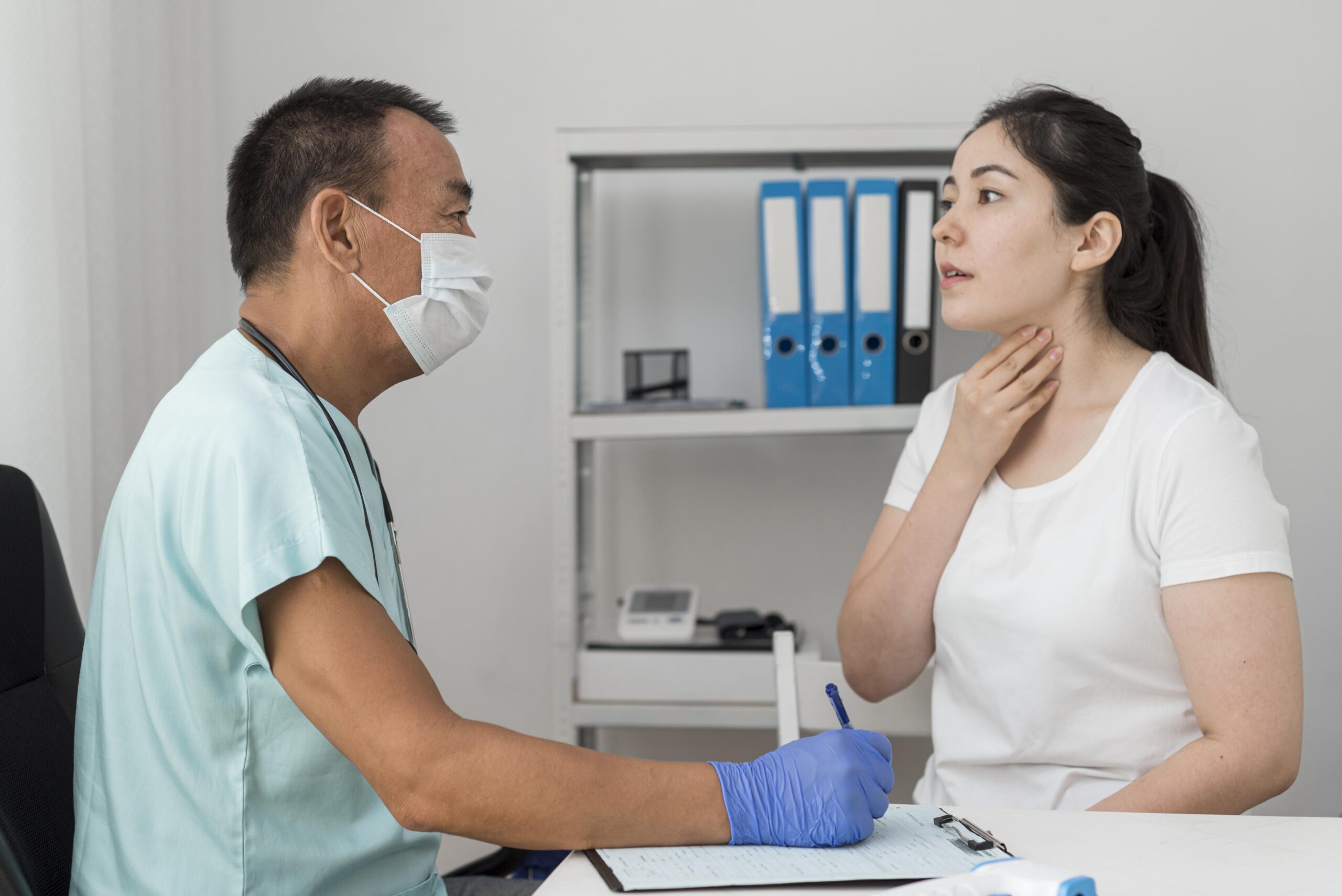
Thyroid Goitre is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck. This condition can result from various causes, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, or benign nodules. While often painless, a goitre can lead to noticeable swelling in the neck and, in some cases, difficulty in breathing or swallowing.
Symptoms of Thyroid Goitre
- Visible Neck Swelling: A noticeable bulge in the neck area.
Breathing Difficulties: Compression of the windpipe leading to shortness of breath.
Swallowing Issues: Difficulty swallowing due to pressure on the esophagus.
Coughing or Hoarseness: Persistent cough or changes in voice quality.
Thyroid Dysfunction Symptoms: Fatigue, weight changes, or temperature sensitivity if the goitre affects hormone production.